The terms ‘capital’ and revenue are two of the most fundamental concepts in business. These ideas are the foundation of a country’s economy. It is critical to draw specific conclusions about income collections and related expenditures based on our country’s financial situation, as this impacts its financial health.
The revenue and capital accounts help us understand national income and expenditure better. Let’s learn more about these concepts in-depth and check revenue vs capital account.
What does a Revenue Account mean?
The term revenue account refers to an account with a credit balance. It includes all government revenue receipts like tax revenues, often known as current receipts.
These receipts include tax revenues and other government revenues. Tax revenues are the funds raised by governments through direct and indirect taxes and charges.
Examples include Income tax, corporate tax, and other direct taxes. Excise duties, customs duties, and service taxes are indirect taxes. Other sources of revenue include interest, dividends, profits from public sector units, fees, fines, and other forms of investment income.
Types of revenue accounts
The following revenue types can appear on an income statement.
Operating revenues
Operating revenue is the money generated by a company’s primary business operations. It usually accounts for a more significant portion of its total revenue. Companies’ operating revenues vary depending on their business type and industry. The following are some instances of operating revenues:
Sales
When a company sells items or services to customers and receives money in return, it records the transaction as its sales revenue.
Rents
When property owners rent out houses, apartments, buildings, and land to tenants, they get rental revenue from the rental contract.
Professional services
The money received by professionals in any sector who give consulting services to clients is known as professional service revenues.
Non-operating revenues
When a firm makes money from activities unrelated to its primary business operations, they earn Non-operating revenues. The following are examples of such revenue:
Interest revenue
Interest revenue is the money a company makes through investments, bank deposits, and repayments and interest on borrowed funds.
Asset sales
Asset sales revenue refers to the one-time proceeds received when a corporation sells its assets and equipment.
What does a Capital Account mean?
The Capital account is the second type of account associated with the government. As the name implies, a capital account keeps track of the government’s capital assets and liabilities. It contains the government’s payments and capital receipts.
So, what may the government’s assets and liabilities be? To put it another way, they’re just like any other company. A company’s capital is the money or liquid assets it earns throughout its operations. The capital account balance determines whether a country is a net exporter or importer of capital.
Types of Capital Accounts
A sole proprietor is the sole owner of a company. The proprietor’s capital account is shown as the owner’s in the company balance statement.
Partners hold capital accounts in a firm or a limited liability partnership (LLP). When an individual joins, they make a financial commitment to the company and invest in it. The capital share of each partner in the partnership agreement or LLP operating agreement determines the calculation of their share of gains and losses.
Shareholders own equity in a corporation. They purchase shares and receive dividends based on the number of shares. They also have voting rights based on the shares they own.
What Does Revenue Expenditure Mean?
Employee wages, inventory, rent, electricity, insurance, stationery, postage, and taxes are examples of revenue expenditures incurred by an organization to operate the day-to-day tasks.
These are expenses that do not contribute to the production of assets or reduce a company’s liabilities. It is recurring in nature and essential to keep a business or organization running daily.
What Does Capital Expenditures Mean?
Capital expenditures are significant capital investments made by a corporation to maintain or, more commonly, develop its business and produce new revenues. Long-term assets, which endure longer than a year but often have a useful life of many years, are purchased as part of capital expenditures.
Fixed assets, such as machinery and equipment, are frequently purchased with capital expenditures. As a result, capital expenditures are usually higher in value than revenue expenditures.
Difference between Revenue Expenditure and Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditures are one-time investments of capital made by a government to expand various industries and businesses to produce profits.
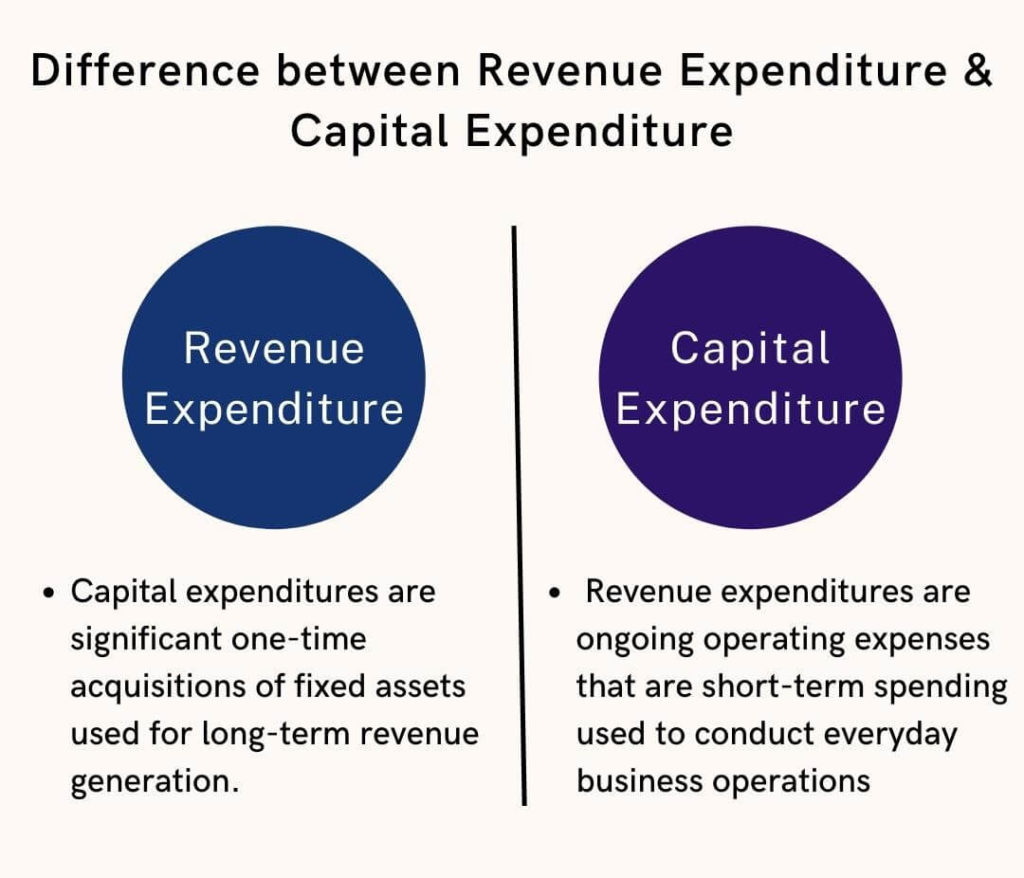
They utilize these expenditures to purchase fixed assets or assets with a long life cycle. These include manufacturing equipment, machinery, and infrastructure-improvement equipment. These assets provide value to the government over their entire life cycle and may or may not have a salvage value. Assets decline over time, and cost depreciation takes place over time rather than all at once.
On the other hand, revenue expenses are more immediate and short-term in nature. They are expenses incurred by the government in its daily activities. These costs are fully charged in the year incurred, and they don’t depreciate over time. They could either be recurring or non-recurring.
Final Thoughts
This article focused on the distinction between revenue and capital account, which are essential concepts to understand in the financial world.
The fundamental difference between them is that capital expenditures are significant one-time acquisitions of fixed assets used for long-term revenue generation. In contrast, revenue expenditures are ongoing operating expenses that are short-term spending used to conduct everyday business operations.






